读写已经关闭的TCP连接会发生什么
读写已经关闭的TCP连接
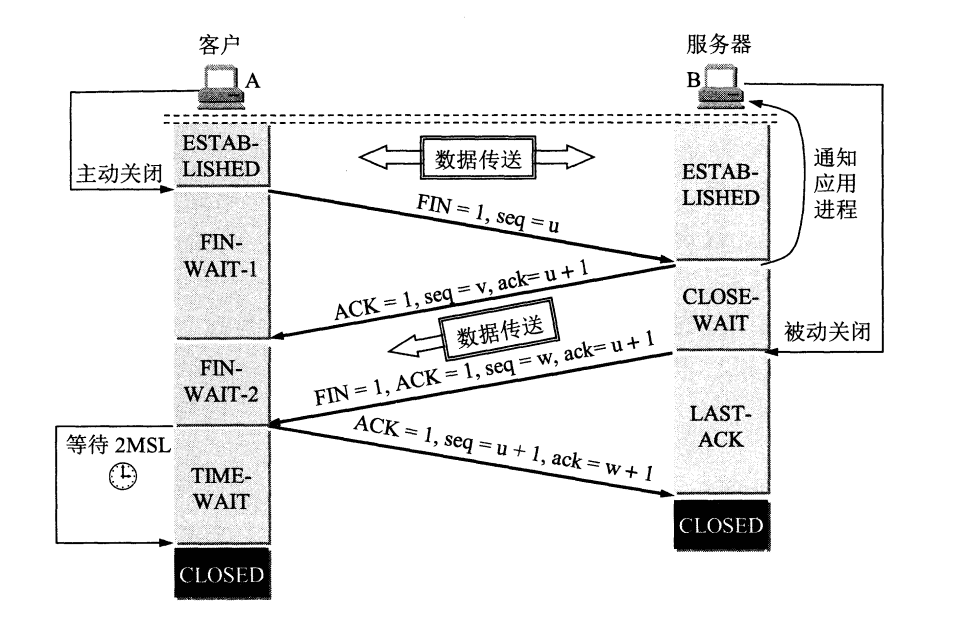
TCP连接状态图
连接关闭的两种方式
关闭一个连接,有两种方式:1.使用四次挥手,正常关闭一个TCP连接。2.在紧急情况下,TCP连接会发送RST报文关闭一个连接。
shutdown与close
shutdown
- int shutdown(int sockfd, int how)
The shutdown() call causes all or part of a full-duplex connection on the socket associated with sockfd to be shut down. If how is SHUT_RD, further receptions will be disallowed. If how is SHUT_WR, further transmissions will be disallowed. If how is SHUT_RDWR, further receptions and transmissions will be disallowed.
If the TCP stack receives a shutdown with SHUT_RD only, it shall mark this connection as no more data expected. Any pending and subsequent
readrequests (regardless whichever thread they are in) will then returned with zero sized result. However, the connection is still active and usable – you can still receive OOB data, for example. Also, the OS will drop any data it receives for this connection. But that is all, no packages will be sent to the other side.If the TCP stack receives a shutdown with SHUT_WR only, it shall mark this connection as no more data can be sent. All pending write requests will be finished, but subsequent write requests will fail. Furthermore, a FIN packet will be sent to another side to inform them we don’t have more data to send.
- SHUT_RD:主动关闭接收端,所有的read都会返回0。由于在TCP连接中不能主动关闭接收端,必须等待对端发送FIN报文,才能关闭当前连接。所以操作系统仍然会收到对端发送的报文,但是这些报文会被丢弃。
- SHUT_WR:主动关闭发送端,操作系统标记当前的连接不可以继续写入。如果写入该连接,会产生SIGPIPE信号。之后操作系统会向对端发送FIN关闭发送端,收到ACK后进入FIN_WAIT2状态,仍然可以接受对端发送的数据。
close
- close():close与SHUT_RDWR相同,同时关闭socket的读端与写端。
写异常
主动关闭写端
- 主动关闭写端,之后再向改socket写入数据,会产生SIGPIPE信号。
对端关闭读端
- 对端仅关闭读端而未关闭写端,此时双方仍都处于ESTABLISHED。对端操作系统仍然会收到发送的报文,但是这些报文会被丢弃。
对端同时关闭读写
- 第一次写入后可以返回,但是发送到对端后,对端处于close_wait状态(并且已经在操作系统内关闭读端),此时发送RST报文,关闭该连接。之后再次写入会产生SIGPIPE信号,再次读返回-1,并且产生错误read error Connection reset by peer, errorno: 104。
读异常
主动关闭读端
- read返回0。
对端关闭写端
- read返回0。
测试读写异常
- 测试过程查看某个端口的连接情况
lsof -i:1234 - 向某个进程发送信号
kill -signal pid
服务端
- 信号SIGINT同时关闭当前连接读写。
- 信号SIGUSR1关闭当前读端。
- 信号SIGUSR2关闭当前写端。
|
|
客户端
- 信号SIGINT同时关闭当前连接写端。
|
|